Main points
- Changing the Wi-Fi channel and separating devices between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz helps optimize Internet speed.
- Updating your router's firmware and checking the Quality of Service (QoS) feature can prevent speed throttling.

Secrets of fast home internet / Depositphotos
When a home network is unstable, we usually blame the provider. However, often the cause of “slow” Internet is the router itself, or more precisely, its basic or outdated settings that we are not used to changing.
Even if the tests show good speed, the real-world experience can be terrible due to small configuration errors that you can fix yourself. 24 Channel tells from personal experience which settings you should pay attention to and what should be changed.
How to make your home router work at full capacity?
Choosing the best channel
The problem is often not a lack of bandwidth, but how the router manages it. One of the main enemies of speed is ” congestion” on Wi-Fi channels . Think of channels as lanes on a highway: if all the neighbors in a house are using the same “lane”, traffic slows down.
Most devices select a channel once when they first turn it on and don't change it again. The 2.4 GHz band has only three non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11), while 5 GHz offers up to 25 such channels, greatly reducing the risk of interference from third-party networks.
To find a “free path”, you should use special mobile applications for Wi-Fi analysis and manually change the channel number in the router's admin panel (usually these are addresses 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
Tip! The WiFi Analyzer app will help you quickly find free channels, check which devices are connected to your WiFi, and even see the signal spread from your router and neighboring devices.
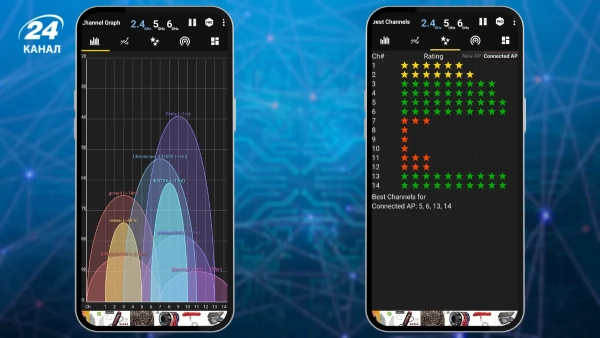
WiFi Analyzer will show which channel is better to choose / Photo 24 Channel
We distribute device connections to different frequencies
It is equally important to correctly distribute devices between frequencies.
- The 2.4 GHz band is a “marathon runner” that passes through walls well, but operates slowly.
- 5 GHz is a “sprinter”, it is much faster, but has a shorter range.
We often connect everything to the first available network, which leaves gaming consoles and streaming devices on the congested 2.4 GHz frequency.
A smart solution would be to separate these networks, giving them different names, and connect laptops and set-top boxes to 5 GHz, while leaving smart bulbs and printers on 2.4 GHz.
Updating the router firmware
Your router's software, or firmware, also needs regular attention. Running on outdated software is like trying to run modern services on a system from a decade ago.
Manufacturers release updates not only for security, but also to optimize traffic and support new speed standards, says Astound. If you ignore this point, even an expensive device can become a “bottleneck” for your data plan.
Most modern models allow you to enable automatic updates in the “Administration” or “System” section, which will allow the system to keep itself up to date.
What else is worth checking in the router settings?
It's also worth checking out the Quality of Service (QoS) feature. In theory, it should help by prioritizing important traffic, but in practice it often hurts.
If you configured QoS years ago on a slow tariff and then switched to gigabit Internet, the router may artificially limit your speed to the old limits.
Additionally, enabling this feature on some models disables hardware acceleration, further reducing performance, says Fortinet.
Finally, don't forget about basic device “hygiene” .
- Regular reboots every few weeks help get rid of software bugs and memory leaks.
- Security also directly affects speed: a weak password or outdated encryption allows unauthorized parties to use your channel, creating unnecessary load.
- Check the list of connected devices in the control panel and disconnect everything unnecessary, and for guests it is better to create a separate network with its own restrictions.
This simple maintenance is often more effective than buying a new router.